奈波爾著作「大河灣」和「畢斯華斯先生的房子」被評為20世紀百大英文小說。他的妻子表示,奈波爾度過充滿驚人創造力和勤奮的一生。
Though often criticized for the way he depicted developing countries in his novels, Naipaul was also praised for writing with an edge and honesty drawn from his rootlessness and discontent.
--
Vidiadhar Surajprasad Naipaul, a Nobel laureate born in Trinidad, published more than 30 books over five decades, ranging from comic novels set in Trinidad and Tobago to memoir and travel writing.
His 1961 novel, A House for Mr Biswas, is seen by many critics as his most important works. The book was based on the life of his father Seepersad, who was a reporter for the Trinidad Guardian.
Vidiadhar Surajprasad was born in Chaguanas, Trinidad. When he was six his family moved to the country’s capital, Port of Spain.
It would later become the setting for his first novel, written in 1959 and titled Miguel Street.
In 1948 he won a government scholarship to read English at Oxford’s University College, where he suffered a nervous breakdown.
It would later become the setting for his first novel, written in 1959 and titled Miguel Street.
In 1948 he won a government scholarship to read English at Oxford’s University College, where he suffered a nervous breakdown.
He married Patricia Hale, whom he met at Oxford in 1955. She died in 1996 and he went on to marry Lady Nadira, who was some 20 years his junior, shortly afterwards.
Throughout his career he was outspoken, notably criticising Tony Blair as well as the famous novel of EM Forster, A Passage To India. He also notoriously fell out with author Paul Theroux, whom he had mentored, but the pair later reunited and resolved their differences.
Among his other well-known works were those on Islamic fundamentalism - the 1981 work Among The Believers and the 1998 book Beyond Belief.
In awarding him the Nobel prize for literature in 2001, the Swedish Academy said he was being honoured “for having united perceptive narrative and incorruptible scrutiny in works that compel us to see the presence of suppressed histories”.

THEGUARDIAN.COM
VS Naipaul, British author, dies aged 85
Nobel and Booker prize-winning writer died surrounded by loved ones in his London home, family confirms
“He read political books. They gave him phrases which he could only speak to himself and use on Shama. They also revealed one region after another of misery and injustice and left him feeling more helpless and more isolated than ever. Then it was that he discovered the solace of Dickens. Without difficulty he transferred characters and settings to people and places he knew. In the grotesques of Dickens everything he feared and suffered from was ridiculed and diminished, so that his own anger, his own contempt became unnecessary, and he was given strength to bear the most difficult part of his day: dressing in the morning, that daily affirmation of faith in oneself, which at times for him was almost like an act of sacrifice.”
― V.S. Naipaul, A House for Mr Biswas
― V.S. Naipaul, A House for Mr Biswas
India's Founding Fathers
By the time Queen Victoria was declared Empress of India, the subcontinent's ancient political traditions had been all but erased.
By SUDHA KOUL
Britain dominated India for almost two centuries—initially through the East India Co. and later directly as the Raj—finally granting it independence in 1947. The Indian anti-colonial struggle was unique in that it reached its goal without violent overthrow. This was one of the great achievements of the nationalist movement's enlightened leadership.In "Righteous Republic: The Political Foundations of Modern India," the historian Ananya Vajpeyi shows how these leaders looked to ancient Indian texts and traditions as they led the nation toward swaraj, or self-rule. The author profiles five prominent anti-colonial leaders and examines how each of them contributed to the nation's successful "search for the self": Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru, who need no introduction; the Bengali poet and Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore; his nephew, the artist Abanindranath Tagore; and B.R. Ambedkar, the architect of the Indian constitution.
India had a glorious past, with millennia of learning, literature, science and art, culture and tradition. Yet by the time the country became the jewel in the crown of Queen Victoria, who was proclaimed Empress of India in 1877, knowledge of the ancient Indic political tradition—the ideas and practices by which "the precolonial kingdoms of the Mughals, the Deccani Sultans, the Nayakas, the Marathas, the Rajputs, and the Sikhs" ruled the subcontinent—had been all but erased thanks to a combination of colonial rule and internal decay. When Indians were told that democracy was a gift of the West, for example, very few questioned the assumption, even though panchayats, or self-governing village bodies, had existed for thousands of years on the subcontinent.
Righteous Republic
By Ananya Vajpeyi(Harvard, 342 pages, $39.95)
The author argues that the essential concepts from which her five Indian leaders drew their ideas for self-rule were mostly indigenous. They include: dharma (the self's aspiration for ethical order); artha (practical purpose); ahimsa (non-violence); duhkha (suffering); viraha (the self's longing); and samvega (the shock of self-recognition). These concepts are distinct from but not in opposition to Western ideals such as equality, liberty and fraternity.
Nehru's quest for national selfhood, for example, revolved around the two central ideas of dharma and artha, or ethical order and pragmatism. The first was exemplified by the inclusive reign, more than two millennia ago, of the Emperor Asoka. The second was embodied in the realpolitik pragmatism of Asoka's grandfather, the Emperor Chandragupta. Aspirational dharma inspired Nehru during the freedom struggle; after independence, he leaned toward purposeful artha.
As Ms. Vajpeyi explains, Nehru married "these opposing vectors in his thought and practice." But his conception of these ideals wasn't merely nostalgic; both had to be reinterpreted for the 20th century. "I should like you to think that the Asokan period in Indian history was essentially an international period," Nehru told the Indian constituent assembly. "In the Asokan era," Nehru instructed, "India's ambassadors went abroad to far countries . . . as ambassadors of peace and culture and goodwill." Asoka's inclusiveness also inspired the clear-cut secularism that Nehru wanted for modern india. "It is strange that anyone should be so foolish," Nehru wrote, "as to think that religion and faith can be thrust down a person's throat at the point of the sword or a bayonet." His fortnightly missives to the chief ministers of the states of the Indian federation make evident his transition from a philosopher into a philosopher-statesman.
When it came time to choose the newly formed Republic of India's national emblems, Nehru selected artifacts unearthed from the Asokan era to visually represent these ethical categories. The state seal of India, for example, is based on the lion capitals that topped Asokan columns and posts. The dharmacakra (wheel of law) at the center of the Indian flag likewise harks back to the Asokan era. "The author of every one of these choices, at the time of Independence, was none other Jawaharlal Nehru," says Ms. Vajpeyi. The appeal of these symbols for Nehru, the author writes, was that in both their ancient and modern incarnations, they represented not just the vastness but also the ethical imperatives of the Indian state.
Noticeably absent from Ms. Vajpeyi's account is the Muslim contribution to the struggle for the Indian self. The author notes a lack of academic or other narrative attention to the quest of Indian Muslims for selfhood and sovereignty and acknowledges her inability to adequately address the subject in her book. India's pre-independence Muslim-Hindu rupture and the subcontinent's descent into a bloodbath at partition reveal the difficulties faced by the Indian founders in uniting a massive, disparate nation to overcome the most powerful empire at the time.
Today the country struggles with sectarian strife as well as corruption and poverty. Ms. Vajpeyi, though, sees hope. The founders' purposes were served by the turn to the past, and she believes the country can learn from the founders' experiences. "By reflecting on the crisis that India went through less than a century ago," the author writes, "we may discover what kinds of soul searching, acts of reading, and interpretive leaps are necessary at such junctures in history."
Ms. Koul is the author of a memoir, "The Tiger Ladies." She has just finished writing "The Kashmir Chronicles," a novel.
-----
精靈之城:德里一年 City of Djinns: A Year in Delhi
p.9 Essex Man 沒注解決
這是近代1980s 英國社會的一重要概念語
現在Wikipedia可以找出這字的說明 新的平均人 工人階段 嚮往中產者
Essex man and Mondeo man are stereotypical figures which were popularised in 1990s England. "Essex man" as a political figure is an example of a type of median voter and was used to help explain the electoral successes of Margaret Thatcher in the previous decade. The closely related "Mondeo man" was identified as the sort of voter the Labour Party needed to attract to win the 1997 election.[1]
City of Djinns (1994) is a travelogue by William Dalrymple about the historical capital of India, Delhi. It is his second book, and culminated as a result of his six-year stay in New Delhi.
City of Djinns was the first product of Dalrymple’s love affair with India, centring on Delhi, a city with ‘a bottomless seam of stories’. Shaped more like a novel than a travel book, he and his wife encounter a teeming cast of characters: his Sikh landlady, taxi drivers, customs officials, and British survivors of the Raj, as well as whirling dervishes and eunuch dancers (‘a strange mix of piety and bawdiness’). Dalrymple describes ancient ruins and the experience of living in the modern city: he goes in search of the history behind the epic stories of the Mahabharata. Still more seriously, he finds evidence of the city’s violent past and present day - the 1857 mutiny against British rule (anticipating The Last Mughal); the Partition massacres in 1947; and the riots after the assassination of Indira Gandhi in 1984.
The book followed his established style of historical digressions, tied in with contemporary events and a multitude of anecdotes.
查一下 這是2007年貼文
2009/4 我從朋友了解2008年買的黃道琳
藏書 是
譯者已逝 (Naipaul, India: A Million Mutinies Now 印度:百萬叛變的今天)
之部分藏書
印度三部曲(V. S. Naipaul 台灣: 奈波爾 中國: 奈保爾 奈保爾爵士,2001年諾貝爾文學獎得主。1932年出生于特里尼達島上的一個印度移民家庭。1950年獲獎學金進 入牛津大學攻讀英國文學,1953年取得學位後遷居倫敦,任職英國廣播公司,1957年以《神秘按摩師》正式開 始寫作生涯。 )
現在看這30年前的"悲觀"說法
不知道印度究竟改變多少
因為30年是歷史之一瞬而已
這本台灣先出版約 二年
| 【印度受傷的文明:印度三部曲之二-當代名家旅行文學54】 |
| I S B N:9578278942 |
| 作 者:奈波爾 |
| 精平裝:/頁數 平裝本 / 234頁 |
| 出版社:馬可孛羅 |
| 出版日: 2001/11/10 |
An Area of Darkness (1964)
這本中國先出版約 二年
| 【幽黯國度-當代名家旅行文學29】 |
| I S B N:9867247280 |
| 作 者:奈波爾 |
| 精平裝: 平裝本 |
| 出版社:英屬蓋曼群島商家庭傳媒股份有限 |
| 出版日:2006/03/01 |
India: A Wounded Civilization (1977)
奇 大陸版的翻譯者是....
幽黯國度:記憶與現實交錯的印度之旅
- 作者:[英]V.S.奈保爾著
- 譯者:李永平譯
- 出版社:生活‧讀書‧新知三聯書店
- 出版日期:2003年08月01日
- 語言:簡體中文 ISBN:7108018063
1962年,奈保爾首次踏訪印度-他父祖輩的家園。從孟買、德里、加爾各答,再到他外祖父的故鄉,這個有著暖味身份的“異鄉人”與“過客”,見到的是無處 不在的貧困與丑陋,感受到的是震驚、憤怒、疏離、鄙夷與失落。春了一貫的冷嘲熱諷與孤傲尖酸中,後殖民情境中的印度亂象是那麼的令人無奈與絕望。這一年的 印度之旅其實也是他企圖探詢自己的歷史與身份認同的內心之旅,而他的收獲卻是看到︰印度屬于黑夜-一個已經死亡的世界,一段漫長的旅程。本書被奈保爾寫得 像畫家做的畫,可以說,不論他以何種文學形式書寫,他都是個大師!
India: A Million Mutinies Now (1990)
印度:百萬叛變的今天
- 作者:[英]V.S.奈保爾著
- 譯者:黃道琳譯
- 出版社:生活‧讀書‧新知三聯書店
- 出版日期:2003年08月01日
- 語言:簡體中文 ISBN:7108018748
目錄
第一部
第一章 想像力停駐的地方
第二章 階級
第三章 來自殖民地的人
第四章 追求浪漫傳奇的人
第二部
第五章 達爾湖中的娃娃屋
第六章 中古城市
第七章 進香
第三部
第八章 廢墟狂想曲
第九章 枕上的花環
第十章 緊急狀態
第十一章 還鄉記
尾聲︰奔逃
附錄 奈保爾作品年表
India: A Million Mutinies Now is a book authored by V. S. Naipaul in 1990. It is a travelogue penned during the author's sojourn in his ancestral land — India. It was the third of Naipaul's acclaimed Indian trilogy which includes An Area of Darkness and India: A Wounded Civilization. True to his style, the narration is anecdotal and descriptive.
Naipaul expresses serious misgivings about Indian attitudes and the Indian way of life. On the other hand Naipaul notes the economic growth and its associated emancipation of the various peoples of India The title makes an analogy between the emancipation of millions and the Mutiny of 1857. The book is somewhat optimistic about the country and its peoples.
mu・ti・ny

━━ n. 反乱, 暴動, 反抗.
━━ vt. 反乱を起す, 反抗する ((away)).
 mu・ti・neer
mu・ti・neer
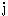
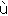
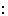
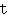
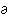
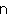
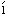
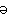

 ━━ n. 暴徒, 反乱者.
━━ n. 暴徒, 反乱者.
 mu・ti・nous
mu・ti・nous
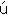
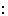
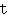
 ━━ a. 暴動[反乱]の; 反抗的.
━━ a. 暴動[反乱]の; 反抗的.
(幽黯國度: 記憶與現實交錯的印度之旅) An Area of Darkness
by V. S. Naipaul, 1964
李永平譯,台北:馬可波羅,2ooo
網路內容簡介:
《幽 黯國度》(一九六四年)是作者在印度遊歷一年,是部具有自傳色彩的作品,記錄他在祖國所見、所聞、所思。作者是出身於千里達島上的一個印度家庭。他的祖父 來自印度,但從不曾向我們描述這個國家的山川文物,在一種非常特殊的層次上,印度一直存留在作者童年生活的背景中。因此,對作者來說,印度並不是真實的 ──它只不過是存在於千里達這個小島外面的茫茫太虛中的一個國家。離開印度後,我們家族的旅程就算終結了。印度是虛懸在時間中的國家。在他心目中,印度依 舊是一個特殊的、與世隔絕的地方;它哺育過我祖父和其他出生在印度、以契約勞工身分來到千里達的鄉親,但即使是這段歷史,後來也湮沒在茫茫太虛中。
當他真實地置身於印度──他的祖國時,童年及成長過程、宗教與種姓階級制度的影響,變得鮮明起來。書中鮮活的記錄著在祖國的印度人及從異地返鄉的印度人生活的點滴,以深刻的角度分析印度人的世界觀和價值觀。
comments
我有大陸的版本。不過今夜翻的是2001年的台版第六刷,可見相當暢銷。不過很少讀到中文的評論。
我想這書處處是珠璣,譬如說[金字塔成為公共廁所。”尾聲:奔逃”的夢相當富哲理。不像正文中斬釘截鐵的論斷,譬如說,「虛誇的自我評價、粗糙的石雕工藝、濫用外國語言(hc案:可惜這必須是不翻譯的原文才能瞭解)--這些現象串連在一起,正好反映出印度的現況。」
(現在我們可以透過NHK等許多印度專題,了解另外的視角。不過詩人所見的許多東西,可能還是直指人心。)
這書探討英國與印度之間的「愛恨情仇」,可能最為精彩部分。
他其實引了許多著名的作品,包括台灣人大部分不知道的一本大部頭回憶錄:Autobiography of an Unknown Indian by Nirad C. Chaudhuri (第289頁)卷首題詞:
“紀念在印度的大英帝國。它把我們視為子民,但我們並不滿足,要求它賦予我們完整的公民權,因為我們心靈中最美好的、充滿生機的一面,是在大英帝國統治下行成和發展的。”
書中說,印度的藝術之衰竭正是在大英帝國統治下的。
Thursday, October 11, 2001
━━ vt. 反乱を起す, 反抗する ((away)).
(幽黯國度: 記憶與現實交錯的印度之旅) An Area of Darkness
by V. S. Naipaul, 1964
李永平譯,台北:馬可波羅,2ooo
網路內容簡介:
《幽 黯國度》(一九六四年)是作者在印度遊歷一年,是部具有自傳色彩的作品,記錄他在祖國所見、所聞、所思。作者是出身於千里達島上的一個印度家庭。他的祖父 來自印度,但從不曾向我們描述這個國家的山川文物,在一種非常特殊的層次上,印度一直存留在作者童年生活的背景中。因此,對作者來說,印度並不是真實的 ──它只不過是存在於千里達這個小島外面的茫茫太虛中的一個國家。離開印度後,我們家族的旅程就算終結了。印度是虛懸在時間中的國家。在他心目中,印度依 舊是一個特殊的、與世隔絕的地方;它哺育過我祖父和其他出生在印度、以契約勞工身分來到千里達的鄉親,但即使是這段歷史,後來也湮沒在茫茫太虛中。
當他真實地置身於印度──他的祖國時,童年及成長過程、宗教與種姓階級制度的影響,變得鮮明起來。書中鮮活的記錄著在祖國的印度人及從異地返鄉的印度人生活的點滴,以深刻的角度分析印度人的世界觀和價值觀。
comments
我有大陸的版本。不過今夜翻的是2001年的台版第六刷,可見相當暢銷。不過很少讀到中文的評論。
我想這書處處是珠璣,譬如說[金字塔成為公共廁所。”尾聲:奔逃”的夢相當富哲理。不像正文中斬釘截鐵的論斷,譬如說,「虛誇的自我評價、粗糙的石雕工藝、濫用外國語言(hc案:可惜這必須是不翻譯的原文才能瞭解)--這些現象串連在一起,正好反映出印度的現況。」
(現在我們可以透過NHK等許多印度專題,了解另外的視角。不過詩人所見的許多東西,可能還是直指人心。)
這書探討英國與印度之間的「愛恨情仇」,可能最為精彩部分。
他其實引了許多著名的作品,包括台灣人大部分不知道的一本大部頭回憶錄:Autobiography of an Unknown Indian by Nirad C. Chaudhuri (第289頁)卷首題詞:
“紀念在印度的大英帝國。它把我們視為子民,但我們並不滿足,要求它賦予我們完整的公民權,因為我們心靈中最美好的、充滿生機的一面,是在大英帝國統治下行成和發展的。”
書中說,印度的藝術之衰竭正是在大英帝國統治下的。
'Incorruptible' V.S. Naipaul wins Nobel Prize in literature
Associated Press WriterSTOCKHOLM, Sweden (AP) -- V.S. Naipaul, a writer
of aching humor and grim reality, won the Nobel Prize in literature on
Thursday for his "incorruptible scrutiny" of postcolonial society and
his critical assessments of Muslim fundamentalism.
Naipaul, 69, a British novelist and essayist who was born in Trinidad to parents of Indian descent, started with the West Indian island as his first subject. He extended his writings to include India, Africa, "America from south to north," and the Islamic communities of Asia and England, according to the citation.
The 215-year-old Swedish Academy singled out his 1987 autobiographical novel, "The Enigma of Arrival," saying the author created an "unrelenting image of the placid collapse of the old colonial ruling culture and the demise of European neighborhoods."
Vidiadhar Surajprasad Naipaul left Trinidad at the age of 18, when he traveled to England to study at Oxford. Naipaul, whose other famous books include "A House for Mr. Biswas" and "A Bend in the River," writes in English.
In fiction and nonfiction, Naipaul described the upheaval of newly independent nations and the people who live with one foot in the remnants of their ancient culture and one in the culture of their colonial masters.
"The history I carried with me, together with the self-awareness that had come with my education and ambition, had sent me into the world with a sense of glory dead," Naipaul wrote in "The Enigma of Arrival."
The Nobel Literature Prize, first awarded to French author Sully Prudhomme in 1901, is worth $943,000 in this centennial year.
Academy head Horace Engdahl reached the laureate after Naipaul's wife, Nadia Khannum Alvi, had to call him several times to get him to the phone at his home in Wiltshire, England. Engdahl described him as a strong individual "which we also think is one of his qualities."
"He was very surprised and I don't think he was pretending. He was surprised because he feels that as a writer he doesn't represent anything but himself," Engdahl said.
Naipaul has the reputation of being a tough-minded, misanthropic man. He does not engage in such literary rituals as publishing parties. In "Sir Vidia's Shadow," a highly unflattering book published in 1998, former friend Paul Theroux wrote that "he elevated crankishness as the proof of his artistic temperament."
Last year's winner was little-known exiled Chinese novelist and playwright Gao Xingjian, a French citizen. His award was denounced by the Chinese government as political. Italy's Dario Fo and Germany's Guenter Grass are other recent winners with strong political views.
Engdahl conceded that this year's choice also might be seen as political in the wake of terror attacks in the United States and the American reaction due to Naipaul's criticism of Muslim fundamentalism in non-Arab countries like Indonesia, Iran, Malaysia and Pakistan.
"The present situation perhaps will make room for a more muted reaction," he said. "I don't think we will have violent protests from the Islamic countries and if they take the care to read his travel books from that part of the world they will realize that his view of Islam is a lot more nuanced."
"What he's really attacking in Islam is a particular trait that it has in common with all cultures that conquerors bring along, that it tends to obliterate the preceding culture," he said.
The 18 lifetime members of the academy make the selection in deep secrecy at one of their weekly Thursday meetings and nominees are not publicly revealed for 50 years, leaving the literary world with only speculation about who might be in the running.
Alfred Nobel, the Swedish industrialist and inventor of dynamite, offered only vague guidance about the prizes in his will, saying only the award should go to those who "shall have conferred the greatest benefit on mankind" and "who shall have produced in the field of literature the most outstanding work in an ideal direction." The awards always are handed out on Dec. 10, the anniversary of Nobel's death in 1896.
The Nobels started Monday with the naming of medicine prize winners, American Leland H. Hartwell and Britons Tim Hunt and Paul Nurse, for work on cell development that could lead to new cancer treatments.
The physics award went Tuesday to German scientist Wolfgang Ketterle and Americans Eric A. Cornell and Carl E. Wieman for creating a new state of matter, an ultra-cold gas known as Bose-Einstein condensate.
On Wednesday, the economics prize went to Americans George A. Akerlof, A. Michael Spence and Joseph E. Stiglitz for developing ways to measure the power of information in a wide range of deals and investments. On the same day, Americans K. Barry Sharpless and William S. Knowles shared the chemistry prize with Ryoji Noyori of Japan for showing how to better control chemical reactions used in producing medicines.
The peace prize is to be announced on Friday in Oslo, Norway.
On the Net:
Nobel site, http://www.nobel.se
Swedish Academy site, http://www.svenskaakademien.se/ENG/index...
***
抵達之謎 The Enigma of Arrival By V.S. Naipaul,
Wiki的封面:
The Enigma of the Arrival and the Afternoon (1912) – Giorgio de Chirico
先讀第五卷 告別儀式 ,可知《薄伽梵歌》Bhagavad Gītā 在印度文化的重量。
小改自:https://timesflowstemmed.com/2018/02/03/the-enigma-of-arrival/
“. . . in the foreground there are two figures, both muffled, one perhaps the person who has arrived, the other perhaps a native of the port. The scene is of desolation and mystery; it speaks of the mystery of arrival.” pp.91-2
Naipaul, 69, a British novelist and essayist who was born in Trinidad to parents of Indian descent, started with the West Indian island as his first subject. He extended his writings to include India, Africa, "America from south to north," and the Islamic communities of Asia and England, according to the citation.
The 215-year-old Swedish Academy singled out his 1987 autobiographical novel, "The Enigma of Arrival," saying the author created an "unrelenting image of the placid collapse of the old colonial ruling culture and the demise of European neighborhoods."
Vidiadhar Surajprasad Naipaul left Trinidad at the age of 18, when he traveled to England to study at Oxford. Naipaul, whose other famous books include "A House for Mr. Biswas" and "A Bend in the River," writes in English.
In fiction and nonfiction, Naipaul described the upheaval of newly independent nations and the people who live with one foot in the remnants of their ancient culture and one in the culture of their colonial masters.
"The history I carried with me, together with the self-awareness that had come with my education and ambition, had sent me into the world with a sense of glory dead," Naipaul wrote in "The Enigma of Arrival."
The Nobel Literature Prize, first awarded to French author Sully Prudhomme in 1901, is worth $943,000 in this centennial year.
Academy head Horace Engdahl reached the laureate after Naipaul's wife, Nadia Khannum Alvi, had to call him several times to get him to the phone at his home in Wiltshire, England. Engdahl described him as a strong individual "which we also think is one of his qualities."
"He was very surprised and I don't think he was pretending. He was surprised because he feels that as a writer he doesn't represent anything but himself," Engdahl said.
Naipaul has the reputation of being a tough-minded, misanthropic man. He does not engage in such literary rituals as publishing parties. In "Sir Vidia's Shadow," a highly unflattering book published in 1998, former friend Paul Theroux wrote that "he elevated crankishness as the proof of his artistic temperament."
Last year's winner was little-known exiled Chinese novelist and playwright Gao Xingjian, a French citizen. His award was denounced by the Chinese government as political. Italy's Dario Fo and Germany's Guenter Grass are other recent winners with strong political views.
Engdahl conceded that this year's choice also might be seen as political in the wake of terror attacks in the United States and the American reaction due to Naipaul's criticism of Muslim fundamentalism in non-Arab countries like Indonesia, Iran, Malaysia and Pakistan.
"The present situation perhaps will make room for a more muted reaction," he said. "I don't think we will have violent protests from the Islamic countries and if they take the care to read his travel books from that part of the world they will realize that his view of Islam is a lot more nuanced."
"What he's really attacking in Islam is a particular trait that it has in common with all cultures that conquerors bring along, that it tends to obliterate the preceding culture," he said.
The 18 lifetime members of the academy make the selection in deep secrecy at one of their weekly Thursday meetings and nominees are not publicly revealed for 50 years, leaving the literary world with only speculation about who might be in the running.
Alfred Nobel, the Swedish industrialist and inventor of dynamite, offered only vague guidance about the prizes in his will, saying only the award should go to those who "shall have conferred the greatest benefit on mankind" and "who shall have produced in the field of literature the most outstanding work in an ideal direction." The awards always are handed out on Dec. 10, the anniversary of Nobel's death in 1896.
The Nobels started Monday with the naming of medicine prize winners, American Leland H. Hartwell and Britons Tim Hunt and Paul Nurse, for work on cell development that could lead to new cancer treatments.
The physics award went Tuesday to German scientist Wolfgang Ketterle and Americans Eric A. Cornell and Carl E. Wieman for creating a new state of matter, an ultra-cold gas known as Bose-Einstein condensate.
On Wednesday, the economics prize went to Americans George A. Akerlof, A. Michael Spence and Joseph E. Stiglitz for developing ways to measure the power of information in a wide range of deals and investments. On the same day, Americans K. Barry Sharpless and William S. Knowles shared the chemistry prize with Ryoji Noyori of Japan for showing how to better control chemical reactions used in producing medicines.
The peace prize is to be announced on Friday in Oslo, Norway.
On the Net:
Nobel site, http://www.nobel.se
Swedish Academy site, http://www.svenskaakademien.se/ENG/index...
***
抵達之謎 The Enigma of Arrival By V.S. Naipaul,
Wiki的封面:
The Enigma of the Arrival and the Afternoon (1912) – Giorgio de Chirico
先讀第五卷 告別儀式 ,可知《薄伽梵歌》Bhagavad Gītā 在印度文化的重量。

First edition
| |
| Author | V. S. Naipaul |
|---|---|
| Translator | Treena Mukherjee (Hindi) |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Language | English |
| Genre | Autobiographical novel |
| Publisher | Viking Press |
Publication date
| March 1987 |
| Media type | Print (Hardback & Paperback) |
| Pages | 318 |
小改自:https://timesflowstemmed.com/2018/02/03/the-enigma-of-arrival/
“. . . in the foreground there are two figures, both muffled, one perhaps the person who has arrived, the other perhaps a native of the port. The scene is of desolation and mystery; it speaks of the mystery of arrival.” pp.91-2
V. S. Naipaul’s novel The Enigma of Arrival refers to this painting by de Chirico, in which Naipaul outlines a story he wishes to write, based on the painting.
It is a personal meditation; a concentrated story about the sadness at the heart of love. Naipaul begins with a dedication: ‘In loving memory of my brother Shiva Naipaul 25 February 1945, Port of Spain 13 August 1985, London’. It is also a reflection on mortality. This is different from the other books I’ve read by Naipaul. In this book, Naipaul creates an intensely spiritual space in which a reader can be blissfully alone.
“He would walk past that muffled figure on the quayside. He would move from that silence and desolation, that blankness, to a gateway or door. He would enter there and be swallowed by the life and noise of a crowded city . . . Gradually there would come to him a feeling that he was getting nowhere, he would lose his sense of mission; he would begin to know only that he was lost. His feeling of adventure would give way to panic. He would want to escape, to get back to the quayside and his ship. But he wouldn’t know how . . . At the moment of crisis he would come upon a door, open it, and find himself back on the quayside of arrival. He has been saved; the world is as he remembered it. Only one thing is missing now. Above the cut-out walls and buildings there is no mast, no sail. The antique ship is gone. The traveller has lived out his life.” pp. 91-2


沒有留言:
張貼留言